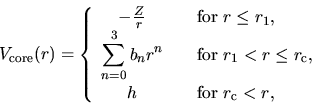 |
(1) |
The pseudo-atomic orbitals are used in the program package, OpenMX, as the primitive basis orbitals. The pseudo-atomic orbitals are generated as follows: first, the SCF calculation is performed in consideration of all electrons under a confinement potential, second, the pseudopotentials are generated, and finally, the pseudo-atomic orbitals for the confinement pseudopotentials are evaluated numerically up to a required excited state. In this section, the generation of the pseudo-atomic orbitals is illustrated. In the file, C.inp, please set the keyword, calc.type, to PAO, and run the executable file, adpack, as follows:
% adpack C.inp
When the run is completed normally, then you find a file, C0.pao, in the
directory, work. In this file, C0.pao, the valence electron density and
the radial parts of the pseudo-atomic orbitals are output.
For your adversaria, the contents of the input file and the results of
all electron SCF calculation are also included.
They are stored in order of log(r), r, and the valence electron density,
and in order of log(r), r, and the radial part 1, the radial part 2,...,
in the flexible date format, respectively.
In Fig. 4, the confinement potential and the pseudo-atomic orbitals
for the s-orbital are shown.
From Fig. 4, we see that the pseudo-atomic orbitals are localized due to
the confinement potential, and the number of nodes increases as
the eigenvalue increases. The confinement potential is made by modifying
the core potential as follows:
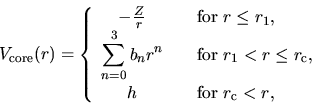 |
(1) |